This is Nissan Motor Company Ltd SWOT analysis. For more information on how to do a SWOT analysis please refer to our article.
Company Overview
| Name | Nissan Motor Company Ltd |
|---|---|
| Founded | December 26, 1933 |
| Logo |  |
| Industries served | Automotive (Cars, Commercial Vehicles) |
| Geographic areas served | Worldwide (more than 100 countries) |
| Headquarters | Nishi-ku, Yokohama, Japan |
| Current CEO | Makoto Uchida |
| Revenue | $87.531 billion (2024) |
| Net Income | $2.944 billion (2024) |
| Employees | 131,719 (2024) |
| Parent | Nissan Group |
| Main Competitors | Bayerische Motoren Werke AG, Chrysler Group LLC, Daimler AG, Ford Motor Company, General Motors Company, Honda Motor Company, Hyundai Motor Company, Tata Motors, Ltd., Toyota Motor Corporation, Volkswagen AG and many other automotive companies. |
Nissan Motor Company Ltd is an automotive manufacturer from Nishi-ku, Japan. The company was founded by Yoshisuke Aikawa in 1934. Nissan struggled to established itself as a global automotive leader and formed a Renault-Nissan alliance in 1999. In 2022 alone, Nissan sold 3.23 million units worldwide.
Nissan sells its cars under 3 different brands: Nissan, Datsun, Infiniti. The company’s main markets are the U.S., China, Russia and Japan.[1]
You can find more information about the business in its official website or Wikipedia’s article.
Nissan SWOT Analysis
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
| 1. Successful Renault-Nissan alliance 2. Effective R&D spending resulting into the best-selling electric vehicle in the world 3. Strong presence in the leading and emerging automotive markets 4. Well-managed company’s operations | 1. Poor marketing and advertising capabilities resulting in poor brand awareness 2. Massive product recalls in the U.S. |
| Opportunities | Threats |
|---|---|
| 1. Increasing government regulations 2. Improving U.S. economy 3. Timing and frequency of new model releases | 1. Increased competition 2. Rising Japanese Yen exchange rates 3. Natural disasters 4. Low fuel prices could negatively impact Leaf sales |
Strengths
1. Successful Renault-Nissan alliance
In 1999, Renault and Nissan have formed an alliance, which is now the longest lasting automotive alliance to date. Renault holds a 43.4% stake in Nissan and Nissan holds a 15% stake in Renault.[1] The alliance is managed by a joint owned Renault-Nissan BV company, which makes sure that companies pursue the strategies that benefit both Renault and Nissan. The alliance allows both companies to:
- Engage in costly R&D activities;
- Invest in the new global projects;
- Negotiate better contracts;
- Enter new markets;
- Share the design, manufacturing and procurement costs.
Figure 1. Nissan-Renault Alliance
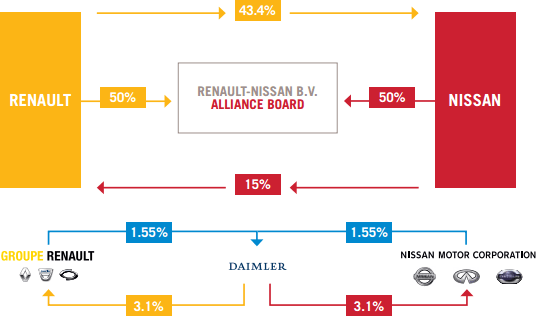
Source: Nissan Global[1]
Renault-Nissan alliance has created synergies that wouldn’t exist otherwise. The group has captured 10% global automotive sales and sold more than 8.5 million cars and other vehicles.
2. Focused R&D spending resulting into the best-selling electric vehicle in the world
Nissan has spent ¥531.9 billion of Japanese yen or US$4.42 billion for R&D in 2015. While this is not the largest amount of money spent for R&D between the automotive companies, it is very well focused by Nissan to a few areas, especially electric vehicles (EV).
Figure 2. Nissan R&D expenditure
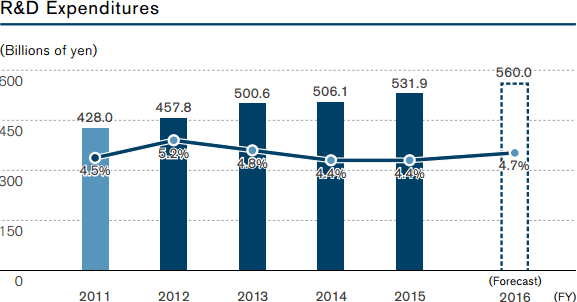
Source: Nissan Annual Report 2016 [2]
Focused R&D spending has allowed the company to produce the best-selling electric vehicle Leaf. In 2015, the company has sold 200,000 units of Leaf and is the leading automotive brand in the EV segment. EV market is expected to grow significantly in the future and Nissan already has an advantage in it.
3. Strong presence in the leading and emerging automotive markets
Nissan through its alliance with Renault and various acquisitions have increased its market share in the global automotive market. The company successfully competes in the U.S. and grows its market share in China, Mexico, Russia, Brazil and other emerging markets.
Figure 3. Renault-Nissan alliance market share
| Country | Market Share |
|---|---|
| United States | 8.5% |
| China | 5.3% |
| France | 30% |
| Japan | 11.7% |
| Russia | 32.3% |
| Mexico | 27.6% |
| United Kingdom | 9.9% |
| Germany | 7.4% |
| Brazil | 9.8% |
| Spain | 18.3% |
Source: Nissan Global[1]
Growing presence in the emerging markets, will allow the company to strengthen its brand and competitive positions in these markets.
4. Well-managed company’s operations
Carlos Ghosn, Nissan’s CEO, has been managing the company since 1999. His management style and reforms inside the ailing Nissan company, have been featured in many business cases. He successfully turned around the company’s operations and returned the company to growth.
Since 2013, Nissan’s revenue grew by 8% annually. In addition, the company’s operating profit and grew by 26.4% and net income by 16% annually. This proves that company’s operations and manufacturing are well lined and that company’s management does a good job running the company.
Weaknesses
1. Poor marketing and advertising capabilities resulting in poor brand awareness
Nissan could improve its marketing and advertising capabilities. The company has spent ¥342.2 billion Japanese yen or US$2.85 billion for advertising in 2015. This is more than what Hyundai, Honda or Audi has spent, yet, the company gained little or no in brand presence for the money spent. No major brand rating agency has included Nissan brand between the world’s top 5 automotive brands or the world’s top 100 largest brands, proving that the company has poor advertising and marketing skills.
Figure 4. Automotive brand ranking by Interbrand (2016)
| Ranking (Automotive) | Brand | Brand Value (in US$ billions) | Overall ranking in 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Toyota | 53.6 | 5 |
| 2 | Mercedes-Benz | 43.5 | 9 |
| 3 | BMW | 41.5 | 11 |
| 4 | Honda | 22.1 | 21 |
| 5 | Ford | 13 | 31 |
| 6 | Hyundai | 12.5 | 35 |
| 7 | Audi | 11.8 | 38 |
| 8 | Volkswagen | 11.4 | 40 |
| 9 | Nissan | 11.1 | 43 |
| 10 | Porsche | 9.5 | 50 |
Source: Interbrand[3]
2. Massive product recalls in the U.S.
The U.S. is the largest Nissan’s market and product recalls seriously damage the company’s brand and sales in the country. In 2015, the company issued recalls for 930,000 Nissan Altima’s models[4] and 768,000 various SUVs and crossovers models. In 2016, the company has recalled 3.53 million various cars’ models over safety bag issues. Every automotive company is affected by product recalls to some extent. Nonetheless, Nissan’s massive recalls are some of the biggest and, unfortunately, concentrated in one market, thus, damaging the company’s brand significantly.
Opportunities
1. Increasing government regulations
Many governments around the world are committed to reducing the greenhouse gas emissions and are encouraging fuel efficiency initiatives. Such environmental initiatives may increase production costs for the car manufacturers and these costs will be either passed to price sensitive consumers or will decrease the company’s profits. Nissan may take advantage of this by introducing more car models running only on electricity and bypassing all the government regulations associated with the greenhouse gas emissions.
2. Improving U.S. economy
Signs of an improving economy and rising consumer confidence have been reflected in the strongest increase in new vehicle sales for more than a decade in the U.S. market. 17.5 million new units were sold in 2015, a 5.7% increase over 2014. Interest rates in the U.S. have been low for several years and are forecast to remain that way for the foreseeable future. In such economic conditions, Nissan has an opportunity to capture the higher market share and increase its sales in the U.S. automotive market.
3. Timing and frequency of new model releases
The market share of the automotive companies is significantly impacted by the timing and frequency of new model releases. Historically, new models have tended to have major upgrades every 4 or 5 years with only minor modifications in between. However, due to the rising consumer expectations in relation to in-car technology and the competitive nature of the industry, there is an argument to release upgraded models more frequently. Nissan is well-positioned to be able to do this.
Threats
1. Increased competition
Nissan is faced with an ever increased competition from the traditional automotive companies and the new players. In China, one of the key company’s markets, new home based Chinese manufacturers are competing by offering lower prices and the similar features. Nissan’s international rivals, such as Toyota, Ford, General Motors and Volkswagen, all have bigger budgets and higher brand recognition and could easily expand in China, U.S. and Europe’s markets by taking the market share from Nissan.
New companies, such as Tesla with its electric cars is competing directly against Nissan’s Leaf. In addition, Google, which tries to build self-driving cars are also threatening the traditional automotive industry. The competition is further fueled by the fact that the global automotive production capacity far exceeds the demand. In 2015, there was an estimated global excess production capacity of 31 million units.[6]
2. Rising Japanese Yen exchange rates
More than 50% of Nissan’s revenue come from the international markets, which means that the company has to convert foreign currencies to Japanese Yen in order to calculate its revenues and send profits back to Japan. Currency rates are volatile and company’s profits and revenue highly depend on the fluctuating exchange rates. The company cannot control currency exchange rates, therefore it is at risk, if Japanese Yen exchange rates would start to rise. In this case, the company’s profits would decrease significantly.
3. Natural disasters
Nissan has manufacturing facilities in Japan, Thailand, China and Indonesia. These countries, including others, are often subject to natural disasters that disrupt manufacturing processes and result in lower production volumes and profits.
4. Low fuel prices could negatively impact Leaf sales
Currently, fuel prices are the lowest in a decade. Such situation has encouraged consumers to buy big fuel-inefficient vehicles such as SUVs and pickup trucks. The company has its own SUVs and pickup truck lines, but suffers from the decreasing consumer demand for Nissan Leaf cars.
The trend of low fuel prices is likely to stay and Nissan may suffer from investing huge amounts of R&D into electric vehicles, for which the demand may significantly decrease.
Sources
- Nissan Global (2016). Alliance Facts & Figures. Available at: http://www.nissan-global.com/EN/DOCUMENT/PDF/ALLIANCE/HANDBOOK/2016/BookletAlliance2016_GB.pdf Accessed November 5, 2016
- Nissan Motor Company Ltd (2016). Annual Report 2016. Available at: http://www.nissan-global.com/EN/DOCUMENT/PDF/AR/2016/AR16_E_All.pdf Accessed November 5, 2016
- Interbrand (2016). Best Global Brands 2016. Available at: http://interbrand.com/best-brands/best-global-brands/2016/ranking/ Accessed November 5, 2016
- Shepardson, D. (2015). Nissan Is Recalling Nearly 1 Million Altimas. Available at: http://time.com/money/4200576/nissan-altima-recall-hood-latch/ Accessed November 5, 2016
- Krok, A. (2016). Nissan recalls over 3 million US vehicles for airbag issues. Available at: https://www.cnet.com/roadshow/news/nissan-recalls-over-3-million-us-vehicles-for-airbag-issues/ Accessed November 5, 2016
- Strategic Management Insight (2016). Ford SWOT analysis 2016. Available at: https://strategicmanagementinsight.com/swot-analyses/ford-swot-analysis/ Accessed November 5, 2016

