This is Honda Motor Company, Ltd. SWOT analysis. For more information on how to do a SWOT analysis please refer to our article.
Company Overview
| Name | Honda Motor Company, Ltd. |
|---|---|
| Founded | September 24, 1948 |
| Logo |  |
| Industries served | Automotive, Aviation, Robotics, Finance |
| Geographic areas served | Worldwide (more than 100 countries) |
| Headquarters | Minato-ku, Tokyo, Japan |
| Current CEO | Toshihiro Mibe |
| Revenue | $140.959 billion (2024) |
| Net Income | $7.640 billion (2024) |
| Employees | 194,993 (2024) |
| Main Competitors | Bayerische Motoren Werke AG, Chrysler Group LLC, Daimler AG, Ford Motor Company, General Motors Company, Nissan Motor Company, Hyundai Motor Company, Tata Motors, Ltd., Toyota Motor Corporation, Volkswagen AG and many other automotive companies. |
Honda Motor Company (further Honda or Company) is a Japanese motorcycle, automobile, aircraft and engine manufacture. The Company was founded in 1948 by Soichiro Honda, as an automotive parts manufacturer. Honda later moved to manufacturing motorcycles and has become the world’s largest motorcycles manufacturer in 1959.[2]
In 1962, Honda started manufacturing automobiles and was the first company to launch a dedicated luxury brand, Acura, in 1986. The Company is now the 8th largest auto manufacturer in the world.
Over the years, the Company has ventured into many industries and is now manufacturing jets and robots.
Honda always highlighted that its core business is engines and all the products the company has ventured in is built around them. Company has been growing significantly over the past few years, mainly due to its automobile business.
You can find more information about the business in its official website or Wikipedia’s article.
Honda SWOT Analysis
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
| 1. Competence in engine manufacturing – company’s core product 2. Diversified product portfolio 3. Dominance in motorcycle and engine industries leading to a high brand awareness 4. Strong position in Asia’s motorcycle markets | 1. Dependence on North America to generate most of the revenue 2. Low investments in research and development (R&D) leading to innovative products |
| Opportunities | Threats |
|---|---|
| 1. Increasing government regulations 2. Improving U.S. economy 3. Timing and frequency of new model releases 4. Low fuel prices are increasing the demand for pickup trucks and SUVs | 1. Increased competition 2. Rising Japanese Yen exchange rates 3. Natural disasters |
Strengths
1. Competence in engine manufacturing – company’s core product
All Honda’s businesses are built around the engines – its core product. The company’s first engines were built for motorcycles and power equipment, but were later produced for cars and marine vehicles. Honda is the world’s largest engine manufacturer, which produced over 27 million units of engines for automotive, motorcycle, marine, and power equipment products, in 2015.[3]
The company has lots of experience in manufacturing quality and well-performing engines. Its engines are praised for their durability, easiness to start, quietness, fuel efficiency and reliability. According to Reliability Index,[4] Honda’s car engines are some the most reliable in the industry.
Engines are the key to motor products and the company’s competence in manufacturing engines is a competitive advantage few rivals can match.
2. Diversified product portfolio
Honda operates 4 different divisions:
- Motorcycle business (12.3% revenue)
- Automobile business (72.8% revenue)
- Power product and other business (2.3% revenue)
- Financial Services (12.6% revenue)
Honda offers many products to consumers including engines, cars, motorcycles, jets, robots, generators, lawnmowers, water pumps, as well as many other power equipment products. While the cars generate the most revenue for Honda, its overall product portfolio is fairly diversified, when compared to Volkswagen, Toyota, General Motors, or Briggs and Stratton (in an engine industry).
Figure 1. Percentage of Sales Revenue by Business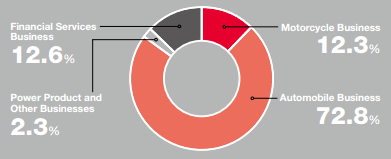
Source: Honda’s Financial Report[1]
3. Dominance in motorcycle and engine industries leading to a high brand awareness
Honda is a huge company dominating in most of the markets it operates in, including engines and motorcycles.
The company is the leading manufacturer of small, general purpose engines for commercial, rental industry, and consumer applications.[5] Honda is also the leading global manufacturer of motorcycles having 22.1% of the total market share in the first half of 2016.[1] Company’s dominance in both of these markets have increased its brand recognition and reputation.
According to Interbrand[6] and Forbes,[7] Honda is the 21st and 23rd most valuable brand in the world, worth US$22.1 billion and US$25.2 billion, respectively. Brand value is closely related to brand awareness and its reputation and only few other companies, such as Toyota, BMW and Mercedes-Benz, can compare with Honda in terms of a brand value.
4. Strong position in Asia’s motorcycle markets
Motorcycle business generates 12.3% of total Honda’s sales and is the third largest revenue group for the company. The company has sold 17,592 units of motorcycles and all-terrain vehicles in 2016 alone and captured 22.1% of the world’s motorcycle market in the first half of 2016.
Asia is the main geographic segment for Honda’s motorcycle business, where the company has sold 15.1 million units or over 88.7% of its total motorcycles, generating ¥1,107.6 billion in revenue.
Asia-Pacific region, which includes such countries as China, India, Vietnam, Thailand, the Philippines, Malaysia, Indonesia, Australia and Japan, is the largest motorcycle region in the world and Honda’s strong position in it is a powerful competitive advantage.
Weaknesses
1. Dependence on North America to generate most of the revenue
Honda depends on North America region, which mainly includes the U.S. and Canada, to generate 55.6% of the company’s total revenue.
Figure 2. Percentage of Sales Revenue by Region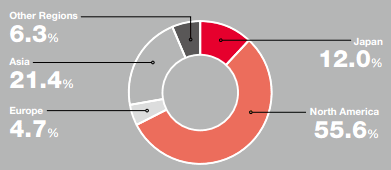
Source: Honda’s Financial Report[1]
Honda’s reliance on North America grew from 49.3% of the total sales in 2014 to 55.6% of the total sales in 2016. At the moment, North America is the main driver behind company’s growth where the motorcycle revenue grew 20% and the automobile revenue grew by 19%. Nonetheless, the U.S. and Canada are saturated markets and Honda will find it hard to maintain the same level of growth in these markets.
The company is also becoming more vulnerable to overall negative changes in North America’s markets.
2. Low investments in research and development (R&D) leading to fewer innovative products
Honda has spent US$5.4 billion for R&D in 2015. This amounted to 4.5% of the company’s total revenue.
Figure 3. Comparison of R&D expenditure – Honda and selected major competitors (in US$ billions)
| Company | 2015 R&D | As a % of revenues | 2014 R&D | As a % of revenues |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Honda | 5.4 | 4.5 | 5 | 4.5 |
| Toyota | 8.4 | 3.7 | 7.6 | 3.5 |
| Volkswagen | 14 | 6.9 | 14 | 7.1 |
| General Motors | 7.5 | 4.9 | 7.4 | 4.7 |
Source: The respective companies’ financial reports[1][5][6][7]
Low investments in R&D lead to fewer innovative products and significantly undermine the company’s abilities to compete in the future. The company should focus its US$5.4 billion R&D investments to certain areas (like Hyundai does), which would erase company’s low R&D budget disadvantage and would result in innovative products.
Opportunities
1. Increasing government regulations
Many governments around the world are committed to reducing the greenhouse gas emissions and are encouraging fuel efficiency initiatives. Such environmental initiatives may increase production costs for the car manufacturers and these costs will be either passed to price sensitive consumers or will decrease the company’s profits. Honda may take advantage of this by introducing more car models running only Hydrogen fuel cells and bypassing all the government regulations associated with the greenhouse gas emissions.
2. Improving U.S. economy
Signs of an improving economy and rising consumer confidence have been reflected in the strongest increase in new vehicle sales for more than a decade in the U.S. market. 17.5 million new units were sold in 2015, a 5.7% increase over 2014. Interest rates in the U.S. have been low for several years and are forecast to remain that way for the foreseeable future. In such economic conditions, Honda has an opportunity to capture higher market share and increase sales in the U.S. automotive market.
3. Timing and frequency of new model releases
The market share of the automotive companies is significantly impacted by the timing and frequency of new model releases. Historically, new models have tended to have major upgrades every 4 or 5 years with only minor modifications in between. However, due to the rising consumer expectations in relation to in-car technology and the competitive nature of the industry, there is an argument to release upgraded models more frequently. Honda is well-positioned to be able to do this.
4. Low fuel prices are increasing the demand for pickup trucks and SUVs
Currently, fuel prices are the lowest in a decade. Such situation has encouraged consumers to buy big fuel-inefficient vehicles such as SUVs and pickup trucks. Traditionally, Honda’s main focus was on smaller cars like Honda Civic and sedans such as Honda Accord, but in the current situation, where fuel prices are low, the company has introduced its next generation pickup truck Ridgeline and redesigned its CR-V sport utility vehicle to meet the demand for the bigger vehicles.
The trend of low fuel prices is likely to stay and Honda should introduce more models of pickup trucks and SUVs to take an advantage of the growing market for these vehicles and to increase company’s profitability.
Threats
1. Increased competition
Honda is faced with an ever increased competition from the traditional automotive companies, the new players and saturation of its main markets. In Asia, the company’s key motorcycle region, markets are nearly saturated. In 2016, Honda’s motorcycle revenue grew by only 5.4% in Asia, compared to 20.3% growth in North America region. The company faces many new entrants in India and China, which offer similar quality motorcycles and scooters for lower price than Honda.
Honda’s automotive business is also experiencing the slowing growth of the automotive markets and the increased competition from the new Chinese manufacturers. The company’s international rivals, such as Toyota, Ford, General Motors, Volkswagen and Hyundai, all have larger budgets and could use them to aggressively take market share from Honda.
New companies, such as Tesla and even Google, which tries to build self-driving cars are also threatening the traditional automotive industry. The competition is further fueled by the fact that the global automotive production capacity far exceeds the demand. In 2015, there was an estimated global excess production capacity of 31 million units.[11]
2. Rising Japanese Yen exchange rates
More than 88% of Honda’s revenue come from international markets, which means that the company has to convert foreign currencies to Japanese Yen in order to calculate its revenues and send the profits back to Japan. Currency rates are volatile and the company’s profits and revenue highly depend on the fluctuating exchange rates. The company cannot control the currency exchange rates, therefore it is at risk, if Japanese Yen exchange rates would start to rise. In such case, the company’s profits would decrease significantly. The company itself identifies this as a key threat that will negatively affect the company over the next few years.
3. Natural disasters
Honda has manufacturing facilities in Japan, Thailand, China and Indonesia. These countries, including others, are often subject to natural disasters that disrupt manufacturing processes and result in lower production volumes and profits.
Sources
- Honda World (2016). Honda Financial Report 2016. Available at: http://world.honda.com/investors/library/annual_report/2016/honda2016ar-all-e.pdf Accessed August 30th, 2016
- Johnson, A. (2005). “Six Men Built the Modern Auto Industry” p.52
- Honda Engines (2016). Why Choose a Honda Engine? Available at: http://engines.honda.com/why/ Accessed August 30th, 2016
- Reliability Index (2016). Manufacturer Ratings. Available at: http://www.reliabilityindex.com/manufacturer/Engine Accessed August 30th, 2016
- Honda Invention (2016). World’s Largest Engine Manufacturer. Available at: http://www.hondainvention.com.au/engine-history.html Accessed August 30th, 2016
- Interbrand (2016). Best Global Brands 2016. Available at: http://interbrand.com/best-brands/best-global-brands/2016/ranking/ Accessed August 30th, 2016
- Forbes (2016). The World’s Most Valuable Brands. Available at: http://www.forbes.com/powerful-brands/list/#tab:rank Accessed August 30th, 2016
- Toyota Motor Corporation (2016). Form 20-F for the Fiscal Year Ended March 31st, 2015. Available at: http://www.toyota-global.com/investors/ir_library/sec/pdf/20-F_201503_final.pdf Accessed August 30th, 2016
- Volkswagen Group (2015). Annual Report 2014. Available at: http://www.volkswagenag.com/content/vwcorp/info_center/en/publications/publications.acq.html/archive-on/icr-financial_publications!annual_reports/index.html Accessed August 30th, 2016
- General Motors Company (2016). Form 10-K for the Fiscal Year Ended December 31st, 2015. Available at: http://www.gm.com/company/investors/sec-filings.html Accessed August 30th, 2016
- Strategic Management Insight (2016). Ford SWOT analysis 2016. Available at: https://strategicmanagementinsight.com/swot-analyses/ford-swot-analysis/ Accessed August 30th, 2016

