People expect some benefit when they use the products and services an organization provides. They want to get some job done, solve a problem, or experience a particular emotion.
It is only when they perceive this benefit as valuable they’ll give something in return – money, time, or attention.
To survive, organizations need to capture some value from their offerings. And value creation lies at the intersection of human interaction with the provider of a service.
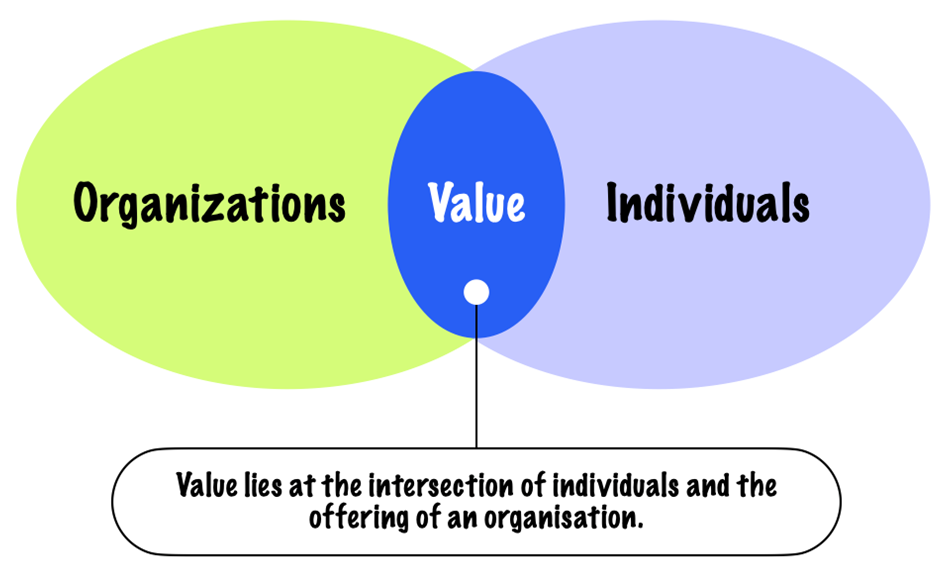
What is a Customer Journey Map
A Customer Journey Map (CJM) belongs to a class of diagrams called Alignment Diagrams[2] that help visualize the story of interaction between individuals and an organization.
They visually illustrate an individual customer’s needs, the series of interactions that are necessary to fulfill those needs, and the resulting emotional states a customer experiences throughout the process.
CJM shows the steps customers go through in engaging with a company, whether it be a product, an online experience, a retail experience, a service, or any combination.
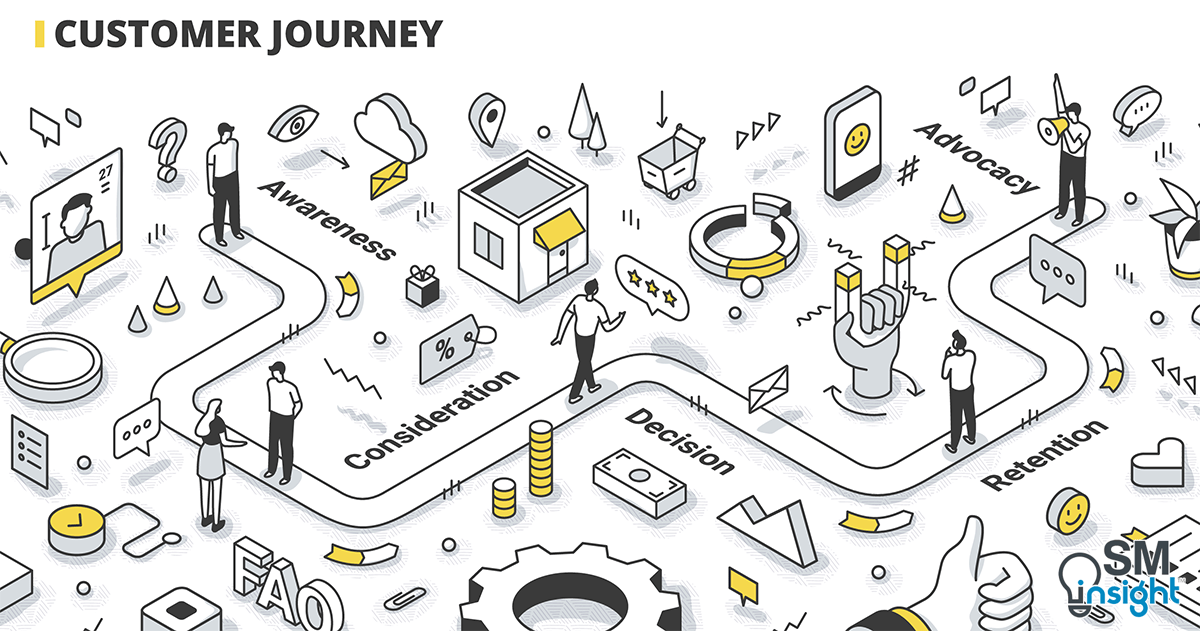
CJMs are also called “cradle-to-grave maps” as they look at the entire arc of engagement. The more touchpoints a company has, the more complicated and necessary they become.
While the exact origin of the term customer journey map (CJM) is unclear, the basic idea of looking across touchpoints has its roots in Jan Carlzon’s concept of moments of truth.[3]
Importance of customer journey map
When most companies focus on customer experience, they think about individual touchpoints – the transactions through which customers interact with parts of the business.
While this is a logical approach and is relatively easy to build into operations, its siloed nature misses the bigger and more important picture – the customer’s end-to-end experience.[4]
A customer’s journey includes many things that happen before, during, and after the experience of a product or service. This journey can be long, stretching across multiple channels and touchpoints, and often lasts days or weeks.
Consider an example of a smartphone purchase, the CJM of which is as shown below.
Touchpoints that left negative emotions are depicted on the bottom of the vertical axis while positive ones are shown above. Each phase of the customer journey is indicated along the horizontal axis and moves from awareness to after-sale:
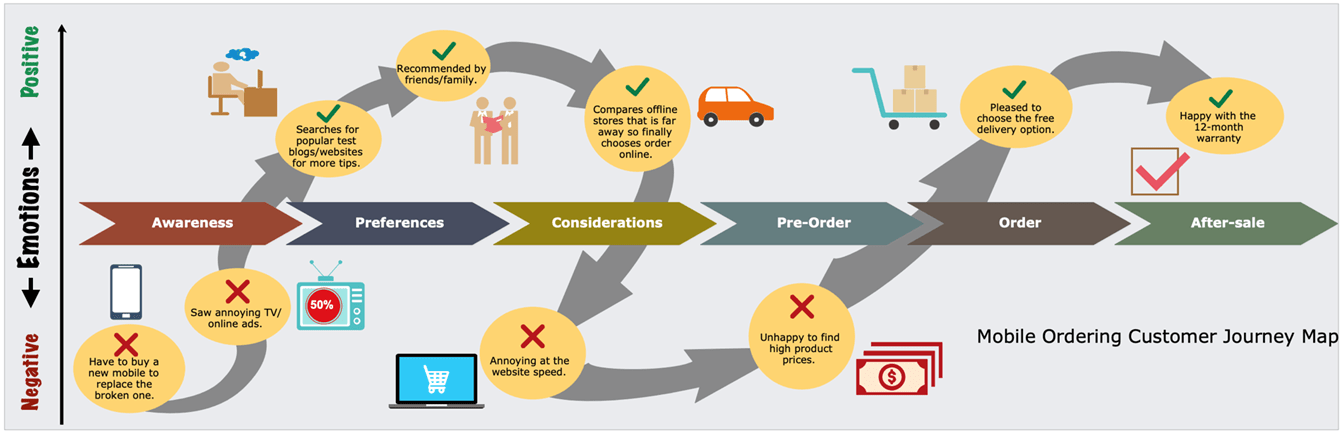
Notice how the customer’s journey involves interactions across multiple touchpoints such as adverts, physical stores, websites, emails, and (sometimes) sales/post-sales support.
A great sales process with a timely delivered smartphone could still lead to a bitter experience if the post-sales support (in case of a defect, for example) is not effective.
Likewise, a poorly designed advert may discourage a customer from considering the purchase in the first place.
Thus, only by looking at the customer’s experience through their own eyes along the entire journey taken can companies begin to understand how to meaningfully improve the overall performance.
Shown below is another, more complex CJM which details the process of installing a broadband and internet service:
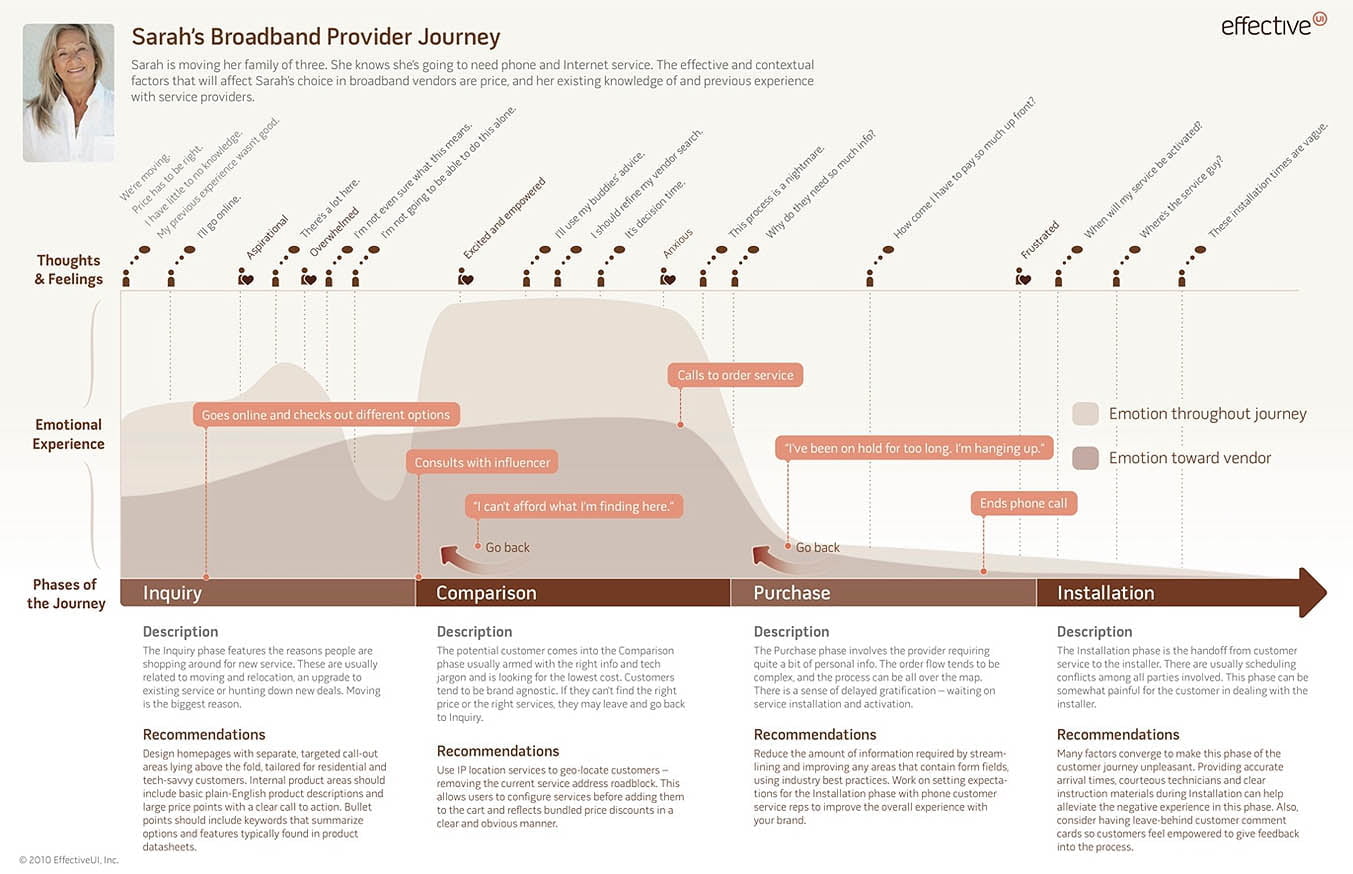
It focuses on the emotional aspects while highlighting the thoughts and feelings a customer typically goes through.
Since creating great experiences is not about individual touchpoint optimization but rather how touchpoints come together into a unified whole, CJMs play a crucial role as a strategic tool to visualize touchpoints and manage them more effectively.
What makes them much more powerful than simply delivering personas and scenarios is their ability to highlight the flow of the customer experience from the ups and downs along the way to those critical pain points where an organization’s attention and focus are most essential.
CJMs help better understand customer loyalty and improve customers’ experiences by answering questions such as:
- How can an organization better engage customers?
- How can it provide value so that customers keep coming back?
- How can it make services more relevant?
Components of a customer journey map
CJMs can range from very simple to complex illustrations that include personas, motivations, emotions, and key activities. To be effective, a CJM must be visually appealing, comprehensive, and understandable.
A CJM consists of the following key elements:
- Customer stages (or timeline): identifies the stages in the customer journey. At a minimum, there are four stages: enquiry, comparison, purchase, and usage. Alternatively, this could also be a finite timeline (e.g., A week, month, year).
- Persona(s): archetypal representations of existing subsets of the customer base who share similar goals, needs, expectations, behaviors, and motivation factors.
- Touchpoints: These are points of contact or interaction between a business and its customers. Information exchange at a touch point could be both unidirectional (e.g.: a banner advert) or bidirectional (physical store).
To align the customer experience and identify pain points between channels and touchpoints, the map should also specify which channels are in focus. - Emotions: CJMs must predict and specify customers’ emotions and feelings. This makes them useful for pinpointing potential pain points and successes.
- Channels: These are means by which interaction takes place. e.g. website, native app, call centre, in-store etc. This is where customers interact.
Optionally, they could also include:
- Barriers and pinpoints: These are areas where a customer is experiencing difficulties or issues with the product or service. This is more relevant when a CJM is developed for “as-is” conditions.
- Customer goals: a customer goal may not always remain constant throughout the journey. Identifying changing goals offers opportunities for improvements in the service.
- Positive experiences: Highlighting what is done well helps stakeholders understand which activities create a positive customer experience and add value.
Creating a customer journey map
While organizations use creative ways to develop customer journey maps, broadly the process includes the following steps:
1. Set objectives
Having a clear goal is a prerequisite to customer journey mapping. A company needs to first decide what it hopes to accomplish through the map, which customers to target (customer segmentation), and which types of experiences it expects the maps to highlight.
Objectives of the map are driven by the company’s strategic goal (e.g., increased revenue or improved customer retention).
For example, if the strategic goal is to improve customer experience, then the objective for the map could highlight key touchpoints, such as website interactions, customer support interactions, and post-purchase experiences, to identify areas for improvement and ultimately improve customer retention.
It is also important to decide on relevant metrics that can be tracked once the customer journey map is created and put to use. Without proper tracking, setting goals doesn’t mean much.
2. Collect customer data and insights
Firms should start the process by taking inventory of the customer knowledge they already have. Data must be gathered from every customer interaction. A marketing automation solution is a great way to collect this information.
For companies that do not have sufficient customer data, Voice of Customer (VoC) is an effective method to gain insights.[7]
Other methods could include mining databases and gathering reports, but the most significant insights will come from the stakeholders themselves. Valuable insights emerge when cross-functional groups are brought together to offer different perspectives on observations and ideas about customers and their experiences.
Data collected at this stage could be both qualitative and quantitative.
3. Distill customer segments into personas and define their goals
With internal and external research in hand, journey mapping leaders need to distill their findings about how customers interact with the company, their expectations from each interaction, and how they feel about each interaction.
Developing a customer persona helps capture the needs, goals, and value a customer brings to a company. Depending on the number of customer segments identified, more than one persona (and by extension, more than one customer map) might be developed.
This helps a company to successfully design experiences that support the specific needs of behaviorally distinct customers.
The benefits of a customer persona over typical customer models are as shown:
| Typical customer models | Persona | |
|---|---|---|
| Research Basis | Quantitative, thousands of data points | Qualitative, dozens of in-depth interviews and observation sessions |
| Demographic and/or psychographic data derived from surveys | Rich narratives describing attitudes, goals, behaviors, preferences, and pet peeves | |
| Buying behavior derived from the purchase history records | Images, audio & video of the users’ environments and the artifacts they use | |
| What they reveal | Value of a customer to the business | How and why they make decisions |
| How they currently behave | The context for their decision-making process, like advice from friends or data from third-party web sites | |
| Where to reach them with targeted messages (e.g., TV networks, online adverts) | Unmet needs and aspirations |
The more accurate a persona is, the more effective the CJM will be.
4. Identify touchpoints
Identifying touchpoints involves generating a list of customer touchpoints and the channels on which those touchpoints currently occur.
For example, the touchpoint could be “pay a bill”, and the channels associated with it could be “pay online”, “pay via mail” or “pay in person”.
Additionally, touchpoints could also be indirect, for example, reviews of a brand that customers read on third-party sites. As each touchpoint can drive customer conversion, it is critical to represent all possibilities.
5. Construct an empathy map
An empathy map is a collaborative visualization used to articulate what is known about a particular type of customer/user.
It externalizes knowledge about them to create a shared understanding of their needs, thereby aiding in decision-making.
Shown below is an example of an empathy map for a customer looking to purchase a television:
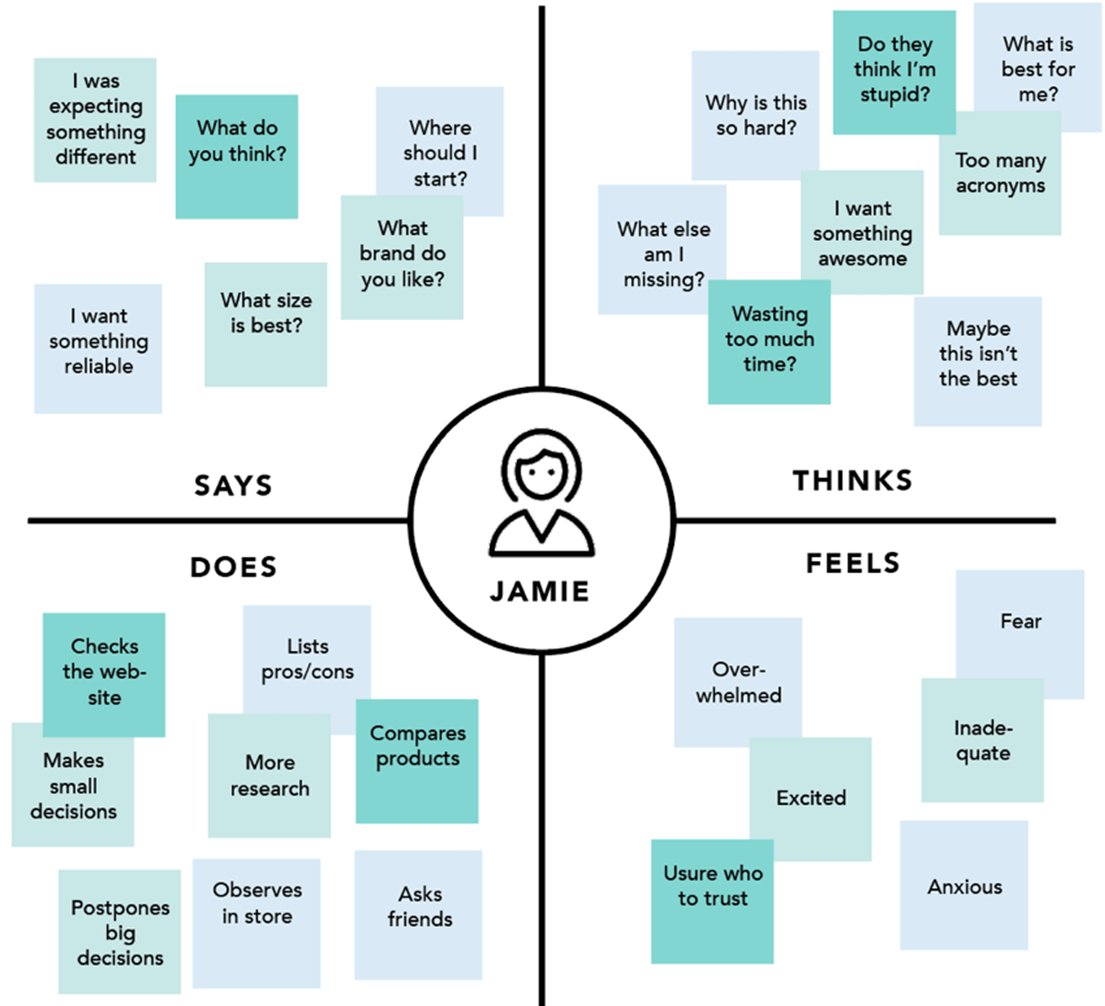
Empathy maps provide a foundation of material to fuel CJMs. They give a well-rounded sense of how it feels to be a particular persona in their experience, specifically focusing on what customers are thinking, feeling, seeing, hearing, saying, and doing.
6. Map the customer journey
This involves putting together all the pieces: timeline, touchpoints, channels, emotions, and even new ideas on how to improve the future customer journey.
The goal is to translate the analysis into a simple visual representation of customer processes, needs, and perceptions. With each interaction, the map should also define customer needs and identify how well the company currently meets those needs.
There are no standard rules or layouts to create a CJM. Even the timeline need not be a standard left-to-right. It could be circular or helical.
The below example shows the LEGO Group’s “experience wheel” which is a CJM built around the three basic stages of an executive’s visit to LEGO offices and the individual experiences that make up each stage.
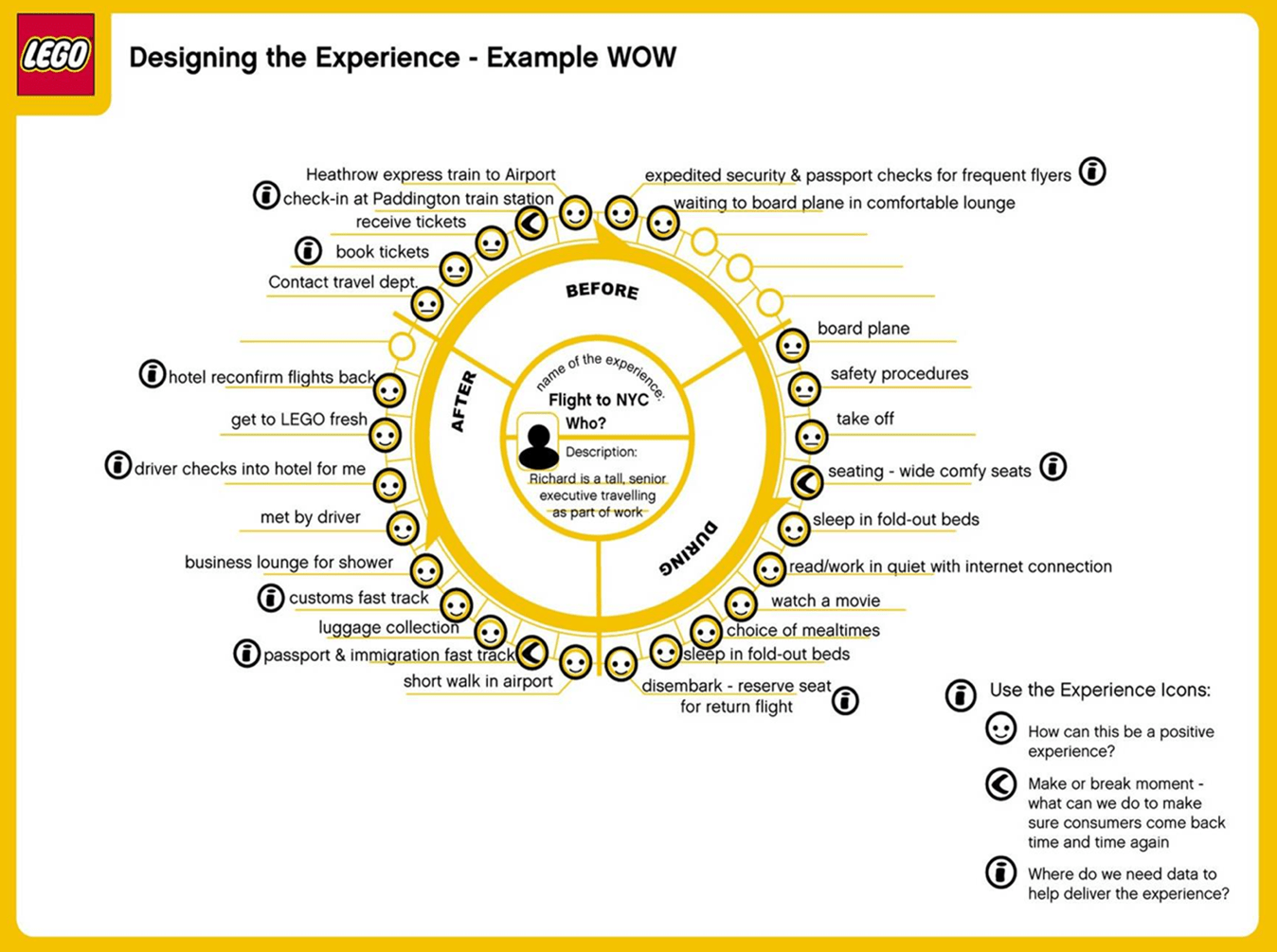
Notice how it starts with the description of a customer persona in the center (Richard, a senior executive in this case). It recognizes the timeline spread across three stages – before, during, and after the flight. It is easy to use and simple to understand.
Also at each interaction, the map defines customer needs and identifies how well the company currently meets those needs (in the form of smileys)
In terms of format, CJMs can be presented as either a comprehensive visual map in print/image form or an interactive digital form featuring clickable elements and embedded videos.
Steps to extract maximum value from CJMs
Developing CJMs won’t automatically realign an organization or improve customer experiences. Most lose momentum and are forgotten along with other research outputs.
To extract value, companies need to follow three practices:[8]
1. Share widely
To set the stage for broad customer experience improvements, the insights from CJMs must be shared with stakeholders across the company. This involves the following steps:
Involve internal stakeholders throughout the CJM process
Executives are more likely to buy into projects that they’re personally involved with. Hence, companies should actively engage decision-makers in the effort.
Those involved in the process early on are also more receptive to final conclusions (even if they are unpleasant) while those who stay out ultimately ignore recommendations.
Highlight key strengths
By design, CJMs are meant to identify problem areas where companies can make improvements. However, too many negatives can leave stakeholders choking.
Hence, to keep executives receptive, and not discourage efforts, a CJM should highlight both strengths as well as weaknesses.
Over time, as companies make improvements in their experiences, they can enjoy watching positive indicators overtake negative ones on their journey maps.
Use the organization’s native language
Companies aren’t accustomed to evaluating themselves from customers’ perspectives. To avoid resistance, it is necessary to tie CJMs to important elements of the existing corporate culture.
For example, explaining to stakeholders how new personas complement rather than replace existing segments.
Bring customer data to life
Engaging presentation techniques can bring CJMs to life.
This could include directly presenting the voice of the customer, showing videos of customers interacting with products or talking about their relationships with the company or audio recordings of customer service calls.
Some companies and consulting firms have used strategies like bringing persona cutouts into review meetings, building up physical rooms with customer research and even getting customers to participate in company meetings.
2. Act on insights
Since customer experience executives don’t manage all the organizational functions affected by the improvements identified in a CJM, this should be driven by leadership.
This calls for methodical identification and prioritization of opportunities while drawing on executive support and past successes. The following steps are important:
Exercise and expand executive support
Leadership should mandate that managers spend time interacting with customers and adopt
customer-focused metrics to measure performance. Without this level of support, customer experience leaders often face resistance from territorial channel and line-of-business leaders.
Another way of gaining executive buy-in is by competing pilot projects that demonstrate the process’s value.
Identify broken moments of truth
CJMs inevitably show companies the areas where they fail to meet their customers’ needs. But having a long list of poor experiences doesn’t tell what’s worth improving.
Companies need to focus on key moments of truth for customers – the interactions that they see as most important.
One way to prioritize is to plot interactions on a simple matrix, showing how important the quality of interactions is for customers:
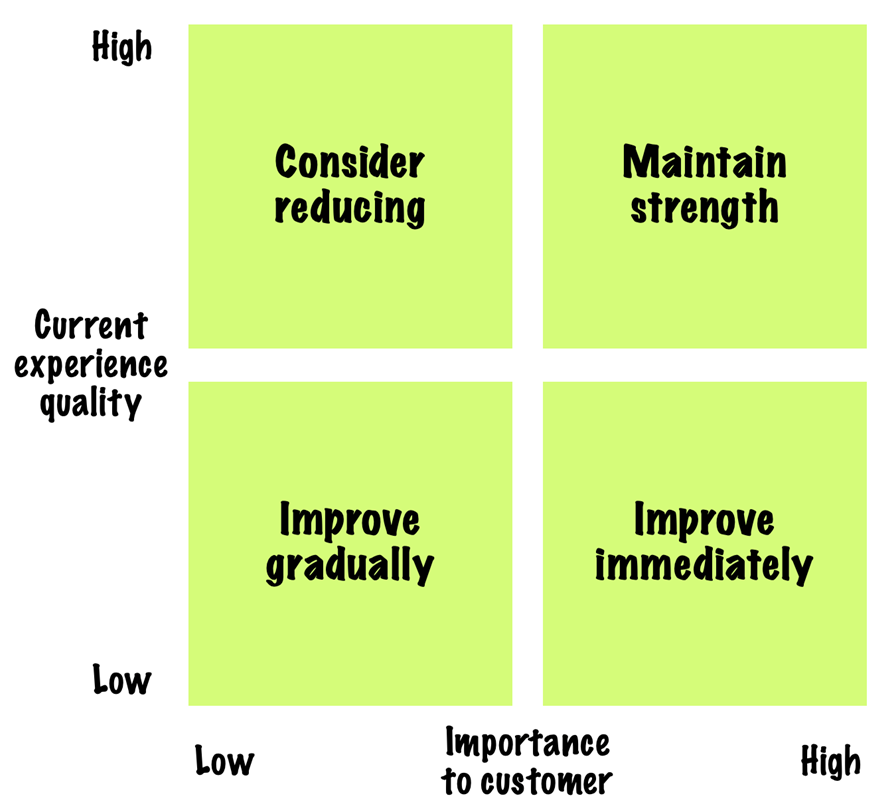
The importance of interaction can be decided through customer research or from simple surveys asking customers to rate experiences in terms of importance and quality.
Companies can also use the Kano Model[11], which is an insightful way of understanding, categorizing, and prioritizing customer requirements.
The model shows the relationship between customer satisfaction and the attributes of products or services being (or to be) offered. It categorizes these attributes into five types:
- Threshold attributes (must-be qualities): These attributes are taken for granted when fulfilled but result in dissatisfaction when not fulfilled.
Customers expect these attributes and view them as basic; it is unlikely that they are going to tell the company about them when asked about quality attributes.
For example, brakes in a car are a basic requirement which goes without saying. - Performance attributes (one-dimensional qualities): These attributes result in satisfaction when fulfilled and dissatisfaction when not fulfilled. These are attributes that are spoken about and the ones in which companies compete.
A good suspension in a car that leads to a comfortable ride is such an attribute. - Excitement attributes (attractive qualities): These attributes provide satisfaction when achieved but do not cause dissatisfaction when not fulfilled. They are not normally expected and thus often unspoken.
Offering a broader choice of colors for a car can potentially delight certain customers, but its absence may not necessarily dissuade them from making a purchase. - Indifferent attributes: These aspects are neither good nor bad and have no effect, positive or negative, on customer satisfaction. For instance, a car equipped with heated seats in a region with a predominantly hot climate.
- Reverse qualities: If these aspects exist, they lead to dissatisfaction; if they do not exist, they do not lead to satisfaction.
- For example, in the case of customers primarily seeking a car for commuting on well-maintained roads, the presence of a four-wheel drive feature can lead to reduced fuel efficiency and discourage them from making a purchase.
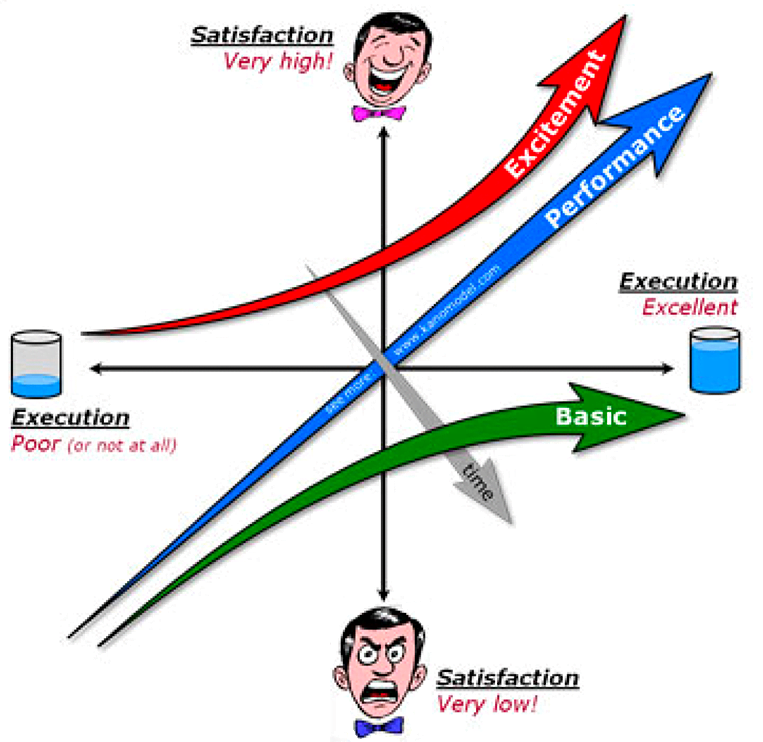
With time, attributes that customers see as excitement (threshold attributes) move down and convert to performance or basic attributes.
For example, a decade ago, a smartphone battery that could last 12 hours was seen as a great feature, but as battery tech improved across generations, that attribute has shifted from delighter to less than a basic need.
This also highlights the fact that what may not be a broken moment of truth today could possibly be one in the future.
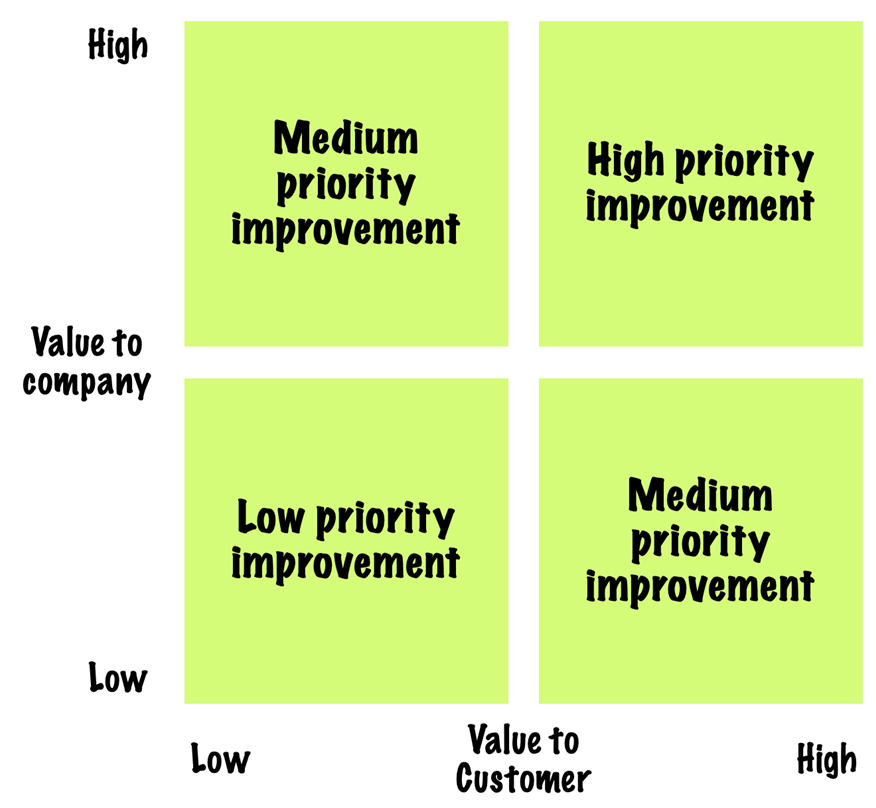
Prioritize opportunities based on value to the company
Even after filtering out low-value opportunities based on customer preference, most companies still face long lists of initiatives.
This can be narrowed down further by balancing their value to customers with elements of business value such as increased revenue, reduced service costs, and differentiation from competitors.
Potential improvements can then be plotted on a simple matrix to highlight improvements with high potential impact.
3. Sustain learnings over time
Companies derive maximum value when they treat the journey mapping process as an ongoing strategic initiative rather than a finite project. The following practices provide discipline to keep journey maps alive over time:
Assign long-term ownership
CJMs need to be linked to the overall strategic planning process of a company with well-defined ownership. Only then, will they remain live and relevant.
Monitor customer feedback and organizational progress over time
CJMs need to be refreshed periodically to remain valid. One way to implement this is by using the maps as the foundation of customer experience data.
Instead of updating findings periodically, fresh customer feedback and performance metrics can be directly fed into the journey maps.
As pointed out by the Kano Model, customer expectations change over time and an updated CJM helps companies sense these shifts early on and take action.
Sources
1. “Mapping Experiences: A Complete Guide to Creating Value through Journeys, Blueprints, and Diagrams”. James Kalbach, https://www.amazon.com/dp/1491923539. Accessed 27 Sep 2023
2. “Alignment Diagrams”. Jim Kalbach, https://boxesandarrows.com/alignment-diagrams/. Accessed 27 Sep 2023
3. “Moments of Truth”. Jan Carlzon, https://www.amazon.com/Moments-Truth-Jan-Carlzon/dp/0060915803. Accessed 25 Sep 2023
4. “From touchpoints to journeys: Seeing the world as customers do”. McKinsey & Company, https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/growth-marketing-and-sales/our-insights/from-touchpoints-to-journeys-seeing-the-world-as-customers-do. Accessed 27 Sep 2023
5. “Mobile Ordering Customer Journey Map Template”. Edrawsoft, https://www.edrawsoft.com/template-mobile-ordering-customer-journey-map.html. Accessed 27 Sep 2023
6. “The Value of Customer Journey Maps: A UX Designer’s Personal Journey”. UX matters (Joel Flom), https://www.uxmatters.com/mt/archives/2011/09/the-value-of-customer-journey-maps-a-ux-designers-personal-journey.php. Accessed 27 Sep 2023
7. “Voice of the customer”. Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Voice_of_the_customer. Accessed 26 Sep 2023
8. “Mapping The Customer Journey”. Forrester (Bruce Temkin), https://www.forrester.com/blogs/10-02-10-mapping_the_customer_journey/. Accessed 26 Sep 2023
9. “Empathy Mapping: The First Step in Design Thinking”. Nielsen Norman Group, https://www.nngroup.com/articles/empathy-mapping/. Accessed 26 Sep 2023
10. “LEGO’s Building Block For Good Experiences”. Bruce Temkin, https://experiencematters.wordpress.com/2009/03/03/legos-building-block-for-good-experiences/. Accessed 26 Sep 2023
11. “What is the Kano Model?”. KanoModel, https://kanomodel.com/. Accessed 27 Sep 2023

